Understanding Credit Card Processing Fees
Credit card processing fees are a critical aspect of accepting payments for businesses of all sizes. These fees can significantly impact your bottom line, making it essential to understand how they work, what factors influence them, and how you can manage or reduce them. In this article, we’ll break down the different types of credit card processing fees, discuss common questions people have, and provide tips to help you navigate this complex landscape.
1. What Are Credit Card Processing Fees?
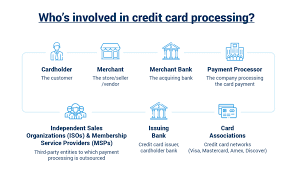
Credit card processing fees are charges that merchants must pay to accept credit and debit card payments. These fees are typically a percentage of each transaction, plus a flat fee. They are paid to various entities involved in the processing of the payment, including the card networks (Visa, MasterCard, etc.), the issuing banks, and the payment processors.
A. Types of Fees
There are various types of fees associated with credit card processing:
- Interchange Fees: Paid to the issuing bank of the customer’s card. These fees vary depending on the card type (credit, debit, rewards, etc.) and the transaction details.
- Assessment Fees: Charged by the card networks (Visa, MasterCard, etc.) for using their payment system. These are typically a small percentage of the transaction.
- Processing Fees: Charged by the payment processor for handling the transaction. These can vary widely depending on the processor and the services provided.
- Flat Fees: A fixed amount added to each transaction, regardless of the transaction size.
Common Questions:
- Why do businesses have to pay credit card processing fees?
These fees cover the cost of securely processing the transaction, preventing fraud, and ensuring that funds are transferred correctly.
2. How Credit Card Processing Fees Are Calculated
The total credit card processing fee for a transaction is the sum of the interchange, assessment, and processing fees. Here’s how each component is calculated:
A. Interchange Fees
Interchange fees are set by the card networks and are typically the largest portion of the processing fees. They depend on factors such as:
- Card Type: Credit cards generally have higher interchange fees than debit cards.
- Transaction Type: Card-present transactions (in-person payments) usually have lower fees than card-not-present transactions (online or phone payments) due to the higher risk of fraud.
- Business Type: Certain industries may have higher or lower fees based on the perceived risk level.
B. Assessment Fees
Assessment fees are charged as a percentage of the transaction amount by the card networks. These fees are generally low but unavoidable. They are used to cover the cost of maintaining and operating the payment network.
C. Processing Fees
Processing fees are charged by the payment processor and can vary depending on the service provider, the volume of transactions, and the specific terms of the contract. Some processors charge a flat rate, while others use a tiered or interchange-plus pricing model.
Common Questions:
- What is the average credit card processing fee?
The average fee is between 1.5% and 3.5% per transaction, but it can vary based on the factors mentioned above.
3. Different Pricing Models for Credit Card Processing Fees
When choosing a payment processor, it’s essential to understand the different pricing models available. These models can significantly affect how much you pay in processing fees.
A. Flat-Rate Pricing
With flat-rate pricing, the processor charges a fixed percentage and a small transaction fee for each sale. This model is straightforward and predictable, making it popular with small businesses.
- Example: 2.75% + $0.10 per transaction.
Pros:
- Easy to understand.
- No surprises or hidden fees.
Cons:
- May be more expensive for high-volume or large-ticket businesses.
B. Interchange-Plus Pricing
In the interchange-plus model, the processor charges the interchange fee plus a fixed markup. This model offers transparency, as you can see exactly how much is going to the issuing bank and how much is the processor’s markup.
- Example: Interchange rate + 0.30% + $0.15 per transaction.
Pros:
- Transparent and often more cost-effective for larger businesses.
- You benefit from lower interchange rates on certain transactions.
Cons:
- Can be more complex to understand.
C. Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing categorizes transactions into different “tiers,” such as qualified, mid-qualified, and non-qualified, each with its rate. The rate you pay depends on the type of card and transaction.
Pros:
- Potentially lower rates for certain transactions.
Cons:
- Lack of transparency, as it’s unclear which transactions fall into which tiers.
- Often results in higher overall costs.
Common Questions:
- Which pricing model is best for my business?
The best pricing model depends on your transaction volume, average ticket size, and business type. Interchange-plus is often recommended for transparency and potential savings.
4. Hidden Costs and Fees to Watch Out For
In addition to the basic processing fees, some payment processors may charge additional fees that can add up over time. Here are some common hidden costs to be aware of:
A. Monthly Fees
Some processors charge a monthly fee for account maintenance, statement fees, or access to customer support.
B. PCI Compliance Fees
PCI compliance is required for businesses that accept credit cards, and some processors charge a fee to help maintain compliance.
C. Early Termination Fees
If you sign a contract with a processor and decide to switch before the term ends, you may be hit with an early termination fee.
D. Chargeback Fees
If a customer disputes a transaction, the processor may charge you a fee to cover the cost of handling the dispute.
E. Batch Processing Fees
Some processors charge a fee every time you submit a batch of transactions for settlement.
Common Questions:
- How can I avoid hidden fees?
Carefully review your contract and ask your processor about all potential fees before signing up.
5. Tips for Reducing Credit Card Processing Fees
High processing fees can eat into your profits, but there are ways to reduce these costs. Here are some tips to help you lower your fees:
A. Negotiate with Your Processor
If you have a high transaction volume, you may be able to negotiate lower rates with your payment processor.
B. Choose the Right Pricing Model
Select a pricing model that aligns with your business’s transaction patterns. For many businesses, interchange-plus pricing offers the best balance of transparency and cost.
C. Encourage Card-Present Transactions
Whenever possible, encourage customers to pay in person, as card-present transactions typically have lower fees than card-not-present transactions.
D. Reduce Chargebacks
Implementing measures to prevent chargebacks, such as verifying customer information and using secure payment methods, can help you avoid costly chargeback fees.
E. Monitor Your Statements
Regularly review your processing statements to ensure you’re not being charged unexpected fees or overpaying for services.
Common Questions:
- Is it possible to completely eliminate credit card processing fees?
While it’s difficult to eliminate fees entirely, careful management and negotiation can significantly reduce them.
6. FAQs About Credit Card Processing Fees
Can I pass credit card processing fees to customers?
Yes, some businesses pass these fees to customers by charging a surcharge. However, this is regulated by state laws, so it’s essential to check your local regulations.
How often do credit card processing fees change?
Interchange rates and other fees can change periodically, typically annually, based on updates from the card networks.
What is PCI compliance, and why do I need it?
PCI compliance refers to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder information. Compliance is required for all businesses that accept credit cards.
Conclusion
Understanding credit card processing fees is crucial for managing your business’s finances effectively. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of fees, pricing models, and potential hidden costs, you can make informed decisions that minimize your expenses. Whether you’re just starting or looking to optimize your existing payment processes, the tips and information provided in this guide will help you navigate the complexities of credit card processing and keep more of your hard-earned revenue.
To read more, Click Here


Leave a Comment